zfarberov.github.io
Saving ESG Bulk Content as CSV Files
Introduction
ESG stands for Environmental Social and Governance (ESG) content. This extra-financial information enables investment processes to identify companies with quality management and reduced risk exposure.
Refinitiv makes ESG available as part of Refinitiv Data PLatform (RDP) that provides simple web based API access to a broad range of content.
Bulk ESG data is scores and measures in efficient weekly bulk files.
In this article we are going to discuss a common use case:
How to process multi-hierarchical, representational JSON ESG Bulk files into flat CSV files that are required by processing by some applications, and preferred for review by a significant
Pre-requisites
Files that we use are available on disk. To learn more of how to requesta and download ESG Bulk content please refer to https://developers.refinitiv.com/en/article-catalog/article/how-to-identify-and-request-esg-bulk-content—python
Flatten ESG Scores File
This is quick to run and very simple in terms of processing required:
fileNameRoot = 'RFT-ESG-Scores-Current-init-2021-05-02'
filedestinationpath = '.\\'
filename = filedestinationpath + fileNameRoot + '.jsonl.gz'
f=gzip.open(filename,'rb')
file_content=f.read()
lines = file_content.splitlines()
df_inter = pd.DataFrame(lines)
df_inter.columns = ['json_element']
df_resolve = df_inter['json_element'].apply(json.loads)
df_resolve
df_final = pd.json_normalize(df_resolve)
df_final['ESGOrganization.Names.Name.OrganizationName'] = pd.json_normalize(df_final['ESGOrganization.Names.Name.OrganizationName'].str[0])
resultspth = filedestinationpath + fileNameRoot + '.csv'
df_final.to_csv(resultspth, index = False)
df_final
Resulting in
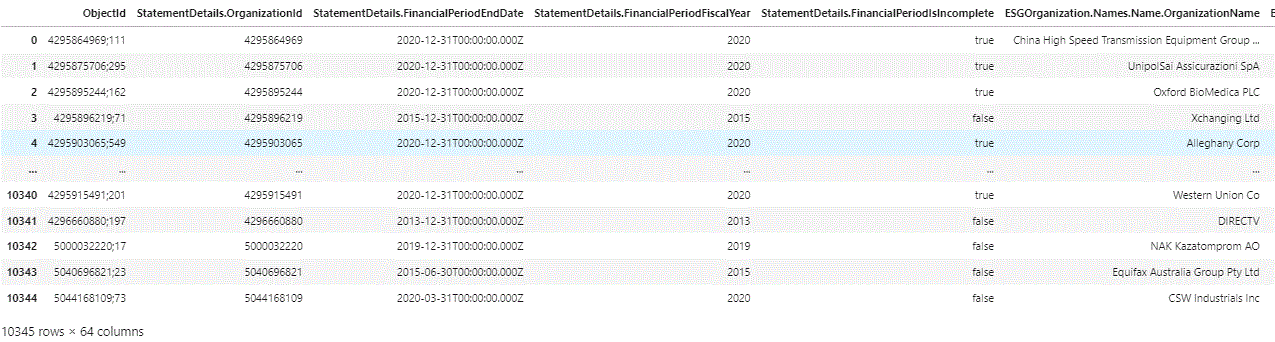
Flatten ESG Symbology SEDOL
Symbology SEDOL carries multiple Quotes as nexted objects, this takes longer to process..
Define flatten_json
We will be using code https://towardsdatascience.com/flattening-json-objects-in-python-f5343c794b10
Rather then https://pypi.org/project/flatten-json/
def flatten_json(nested_json, exclude=['']):
"""Flatten json object with nested keys into a single level.
Args:
nested_json: A nested json object.
exclude: Keys to exclude from output.
Returns:
The flattened json object if successful, None otherwise.
"""
out = {}
def flatten(x, name='', exclude=exclude):
if type(x) is dict:
for a in x:
if a not in exclude: flatten(x[a], name + a + '_')
elif type(x) is list:
i = 0
for a in x:
flatten(a, name + str(i) + '_')
i += 1
else:
out[name[:-1]] = x
flatten(nested_json)
return out
Normalize All
fileNameRoot = 'RFT-ESG-Symbology-SEDOL-Delta-2021-05-13'
#convert specific json to csv
filedestinationpath = '.\\'
filename = filedestinationpath + fileNameRoot + '.jsonl.gz'
f=gzip.open(filename,'rb')
file_content=f.read()
lines = file_content.splitlines()
df_inter = pd.DataFrame(lines)
df_inter.columns = ['json_element']
df_resolve = df_inter['json_element'].apply(json.loads)
df_resolve
df_inter2 = pd.json_normalize(df_resolve)
df_inter2
The result is:
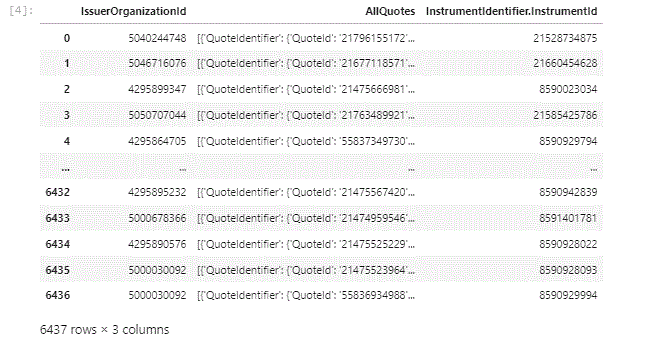 Which is not what we are looking for, yet
Which is not what we are looking for, yet
Normalize Nested
By iterating rows and flattenting AllQuotes column that contains nested lists - this takes longer…
df_accum = pd.DataFrame()
for i in range(0,df_inter2['AllQuotes'].size):
df_accum = df_accum.append(pd.json_normalize(flatten_json(df_inter2['AllQuotes'][i])))
df_accum
This takes a significant chunk of time to process
But at the end the result is:
 Which is flattened, and what we are looking for, all the remains to do is
Which is flattened, and what we are looking for, all the remains to do is
Merge Columns
Merging previously normalized columns and newly created columns originating from flattened AllQuotes
df_fin = df_inter2.merge(df_accum, left_index=True, right_index=True)
df_fin
Delete Nested AllQuotes Column
That we do not need anymore, as the content of it are now fully flattened
df_final = df_fin.drop('AllQuotes', 1)
Save Flattened DataFrame Result To CSV File
And now we are ready to save the flattened output to a file
resultspth = filedestinationpath + fileNameRoot + '.csv'
df_final.to_csv(resultspth, index = False)
df_final